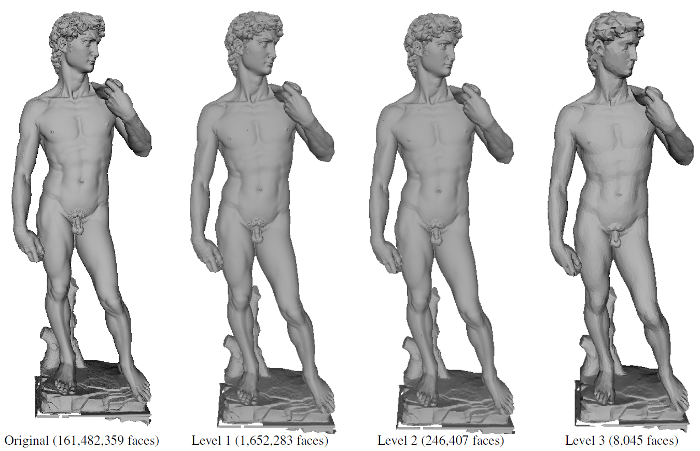
In mesh simplification, in-core based methods using Quadric Error Metric (QEM), which apply a sequence of edge-collapse operations, can generate high-quality meshes while preserving shape features. However, these methods cannot be applied to huge meshes with more than 100 million faces, because they … Continue reading “Out-of-Core Framework for QEM-based Mesh Simplification”
Author: Takashi Kanai
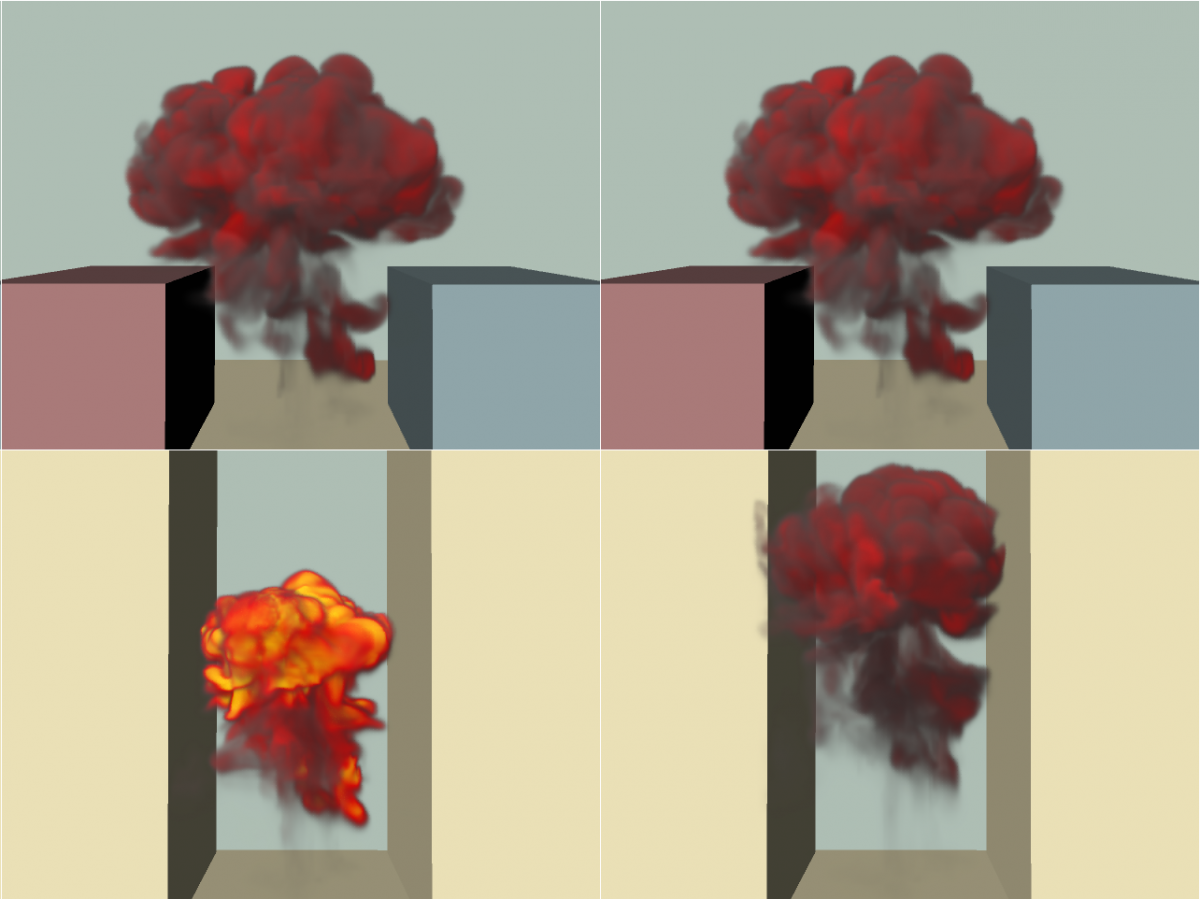
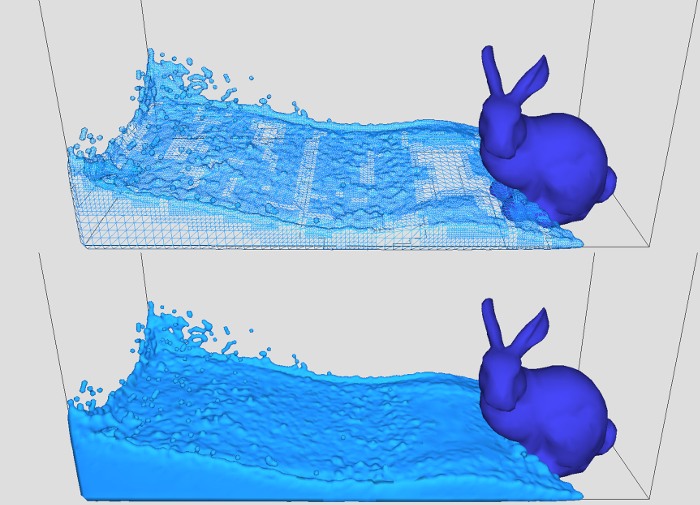
Controlling the Shape and Motion of Plumes in Explosion Simulations
We propose a fluid simulation method with controlling the shape and motion of rising fire and smoke, called plumes, in the incompressible phase of explosion phenomenon. With our method, plumes are generated based on physical phenomenon called entrainment, which strongly characterizes plume behaviors … Continue reading “Controlling the Shape and Motion of Plumes in Explosion Simulations”
VRIPHYS 2014@ブレーメン・ドイツで発表しました.
Sorry, this entry is only available in 日本語.
WSCG 2014@ピルゼン・チェコ共和国で発表しました.
Sorry, this entry is only available in 日本語.
GPU-based Adaptive Surface Reconstruction for Real-time SPH Fluids
We propose a GPU-based adaptive surface reconstruction algorithm for Smoothed-Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) fluids. The adaptive surface is reconstructed from 3-level grids as proposed by [Akinci13]. The novel part of our algorithm is a pattern based approach for crack filling, which is recognized as … Continue reading “GPU-based Adaptive Surface Reconstruction for Real-time SPH Fluids”
VC/GCAD 合同シンポジウム 2013 @青森で研究発表しました.
Sorry, this entry is only available in 日本語.
(社)画像電子学会西田賞を受賞しました.
Sorry, this entry is only available in 日本語.
CAD’12@ナイアガラフォールズ・カナダで発表しました.
Sorry, this entry is only available in 日本語.
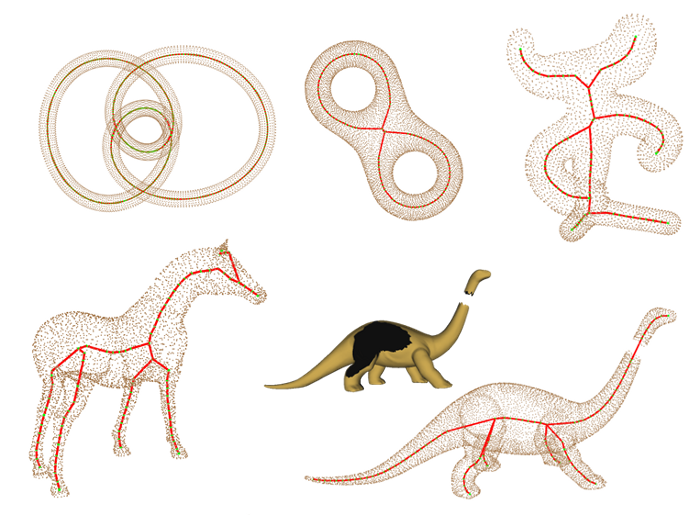
A Robust and Centered Curve Skeleton Extraction from 3D Point Cloud
A curve skeleton of a 3D object is one of the most important structures of the object, which is extremely useful for many computer graphics applications involving in shape analysis. Much research has focused on volumetric and polygonal mesh models. However, only a few have been paid attention to poi … Continue reading “A Robust and Centered Curve Skeleton Extraction from 3D Point Cloud”
インタビュー記事が掲載されました.
Sorry, this entry is only available in 日本語.