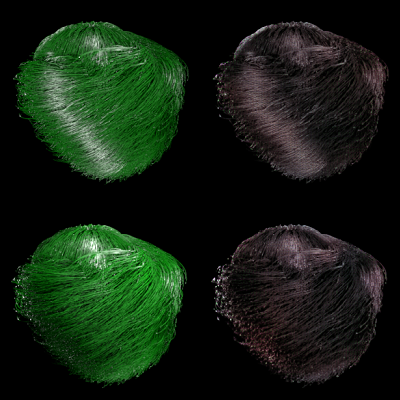
We introduce a GAN-based model for shading photorealistic hair animations. This work try to shade photorealistic hairs by extending the unsupervised Generative Adversarial Networks. Also, our model is much faster than the previous onerous rendering algorithms and produces fewer artifacts than other … Continue reading “A GAN-based Temporally Stable Shading Model for Fast Animation of Photorealistic Hair”
Category: Computer Graphics
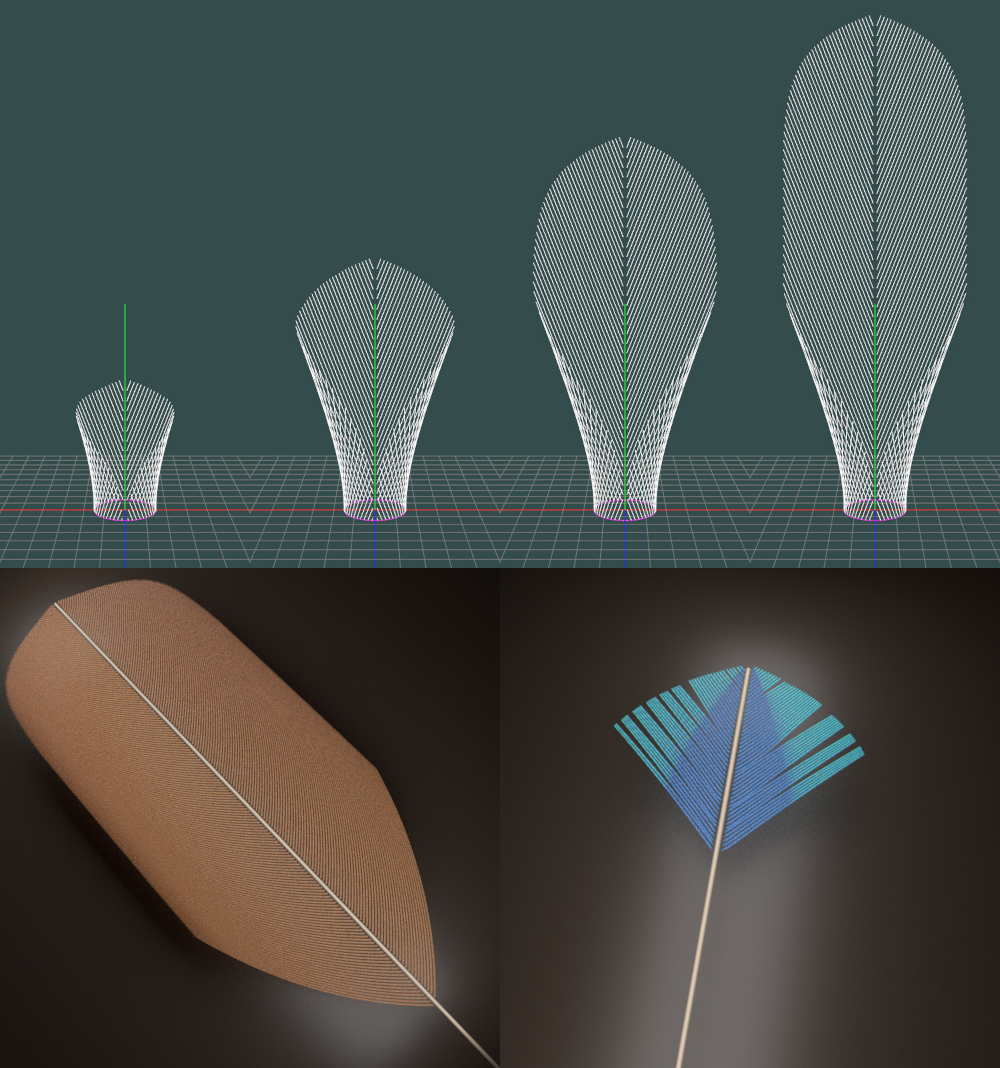
Biological Modeling of Feathers by Morphogenesis Simulation for Computer Graphics
Feathers are sophisticated skin appendages on bird skin, with massive fiber curves (called barbs) branching out from a shaft. Each barb uses its hooklets (called barbules) to further interlock with each other and form two surfaces. We propose a biological modeling scheme that follows the natural fea … Continue reading “Biological Modeling of Feathers by Morphogenesis Simulation for Computer Graphics”
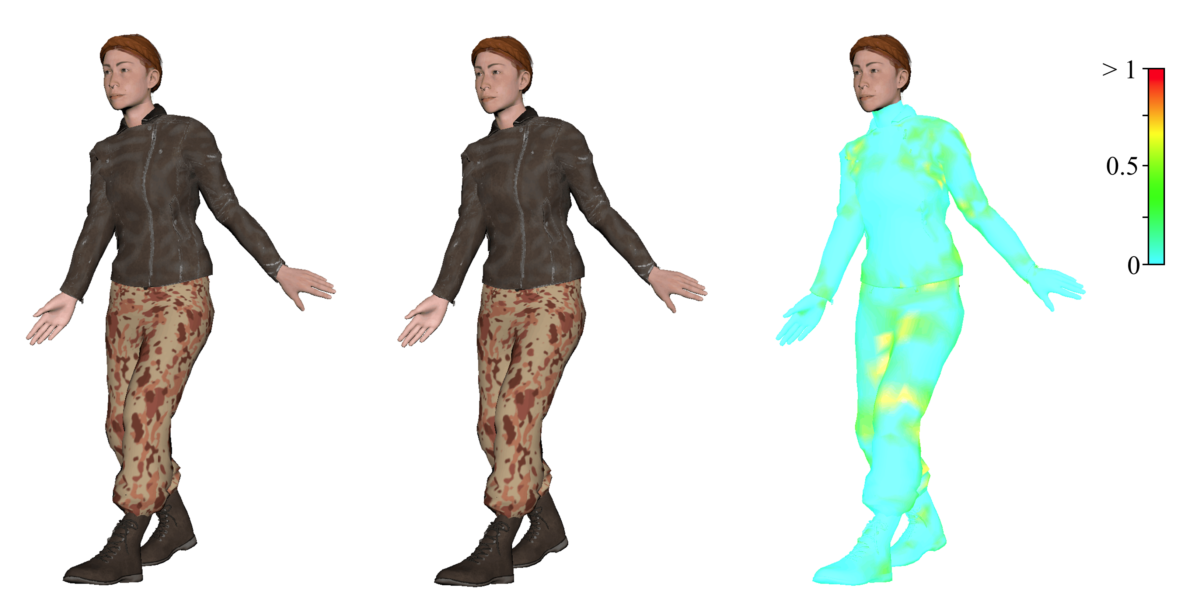
DenseGATs: A Graph-Attention-Based Network for Nonlinear Character Deformation
In animation production, animators always spend significant time and efforts to develop quality deformation systems for characters with complex appearances and details. In order to decrease the time spent repetitively skinning and fine-tuning work, we propose an end-to-end approach to automatically … Continue reading “DenseGATs: A Graph-Attention-Based Network for Nonlinear Character Deformation”
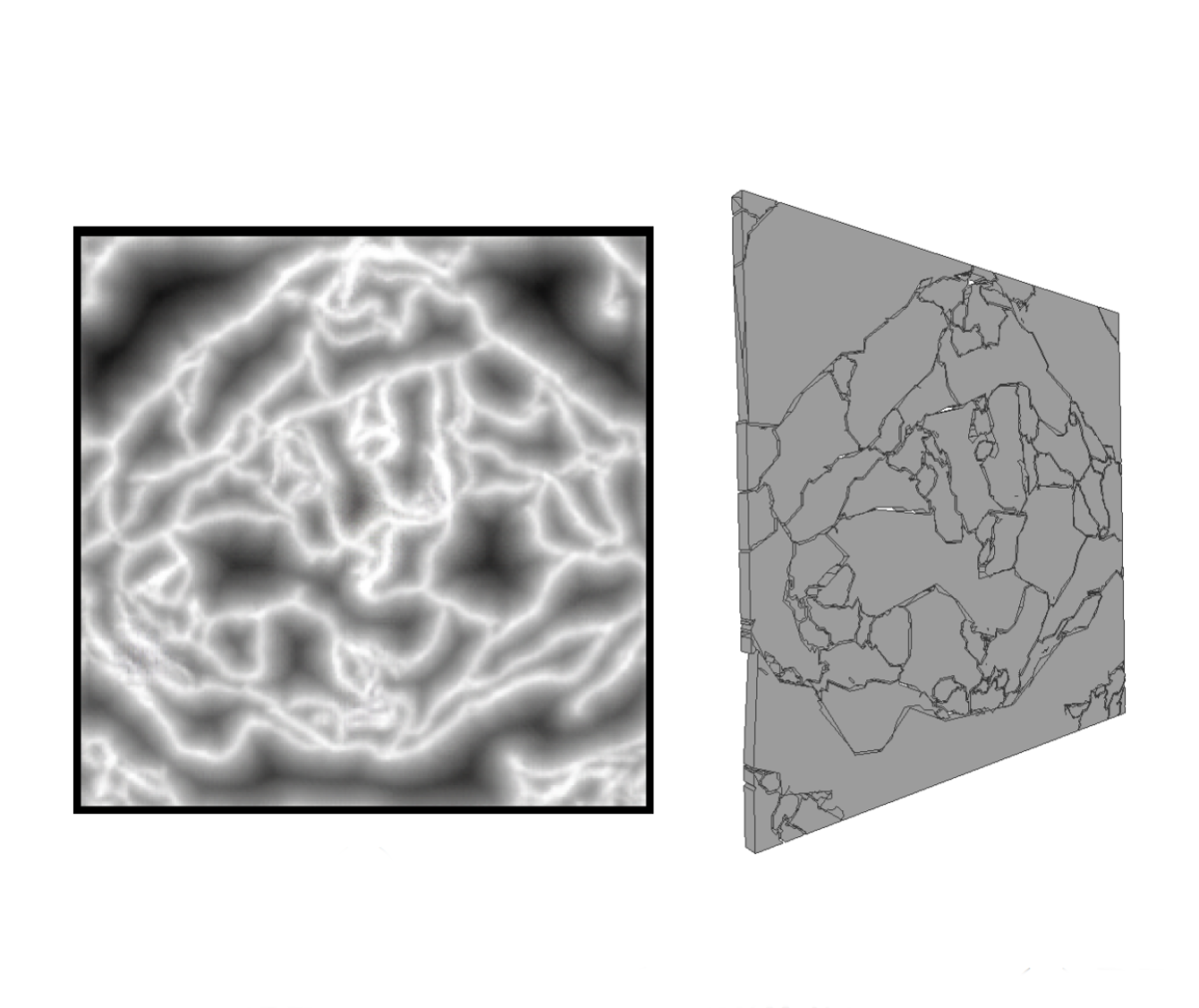
Brittle Fracture Shape Generation of 2D Planes Using Deep Learning
Brittle fracture of plane shape objects, such as glass and concrete, is often seen in the real world. Fracture animation of rigid bodies provides impressive effects by using physics-oriented simulation. However, simulation costs become too high when physics-oriented simulation approaches are chosen … Continue reading “Brittle Fracture Shape Generation of 2D Planes Using Deep Learning”
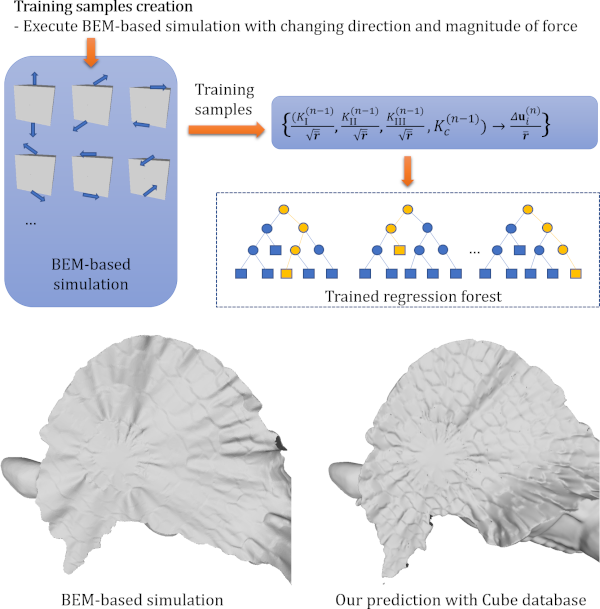
Data-Driven Approach for Simulating Brittle Fracture Surfaces
In this paper, we propose a novel data-driven method that uses a machine learning scheme for formulating fracture simulation with the Boundary Element Method (BEM) as a regression problem. With this method, the crack-opening displacement (COD) of every correlation node is predicted at the next frame … Continue reading “Data-Driven Approach for Simulating Brittle Fracture Surfaces”
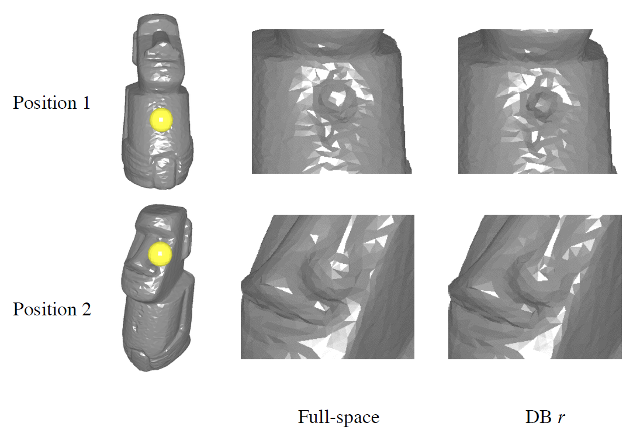
Data-driven Subspace Enrichment for Elastic Deformations with Collisions
We propose an efficient data-driven enrichment approach to adaptively enhance the expressivity of subspaces for elastic deformations with novel collisions. In general, subspace integration method (also known as model reduction) for elastic deformations can greatly increase simulation speed. However, … Continue reading “Data-driven Subspace Enrichment for Elastic Deformations with Collisions”
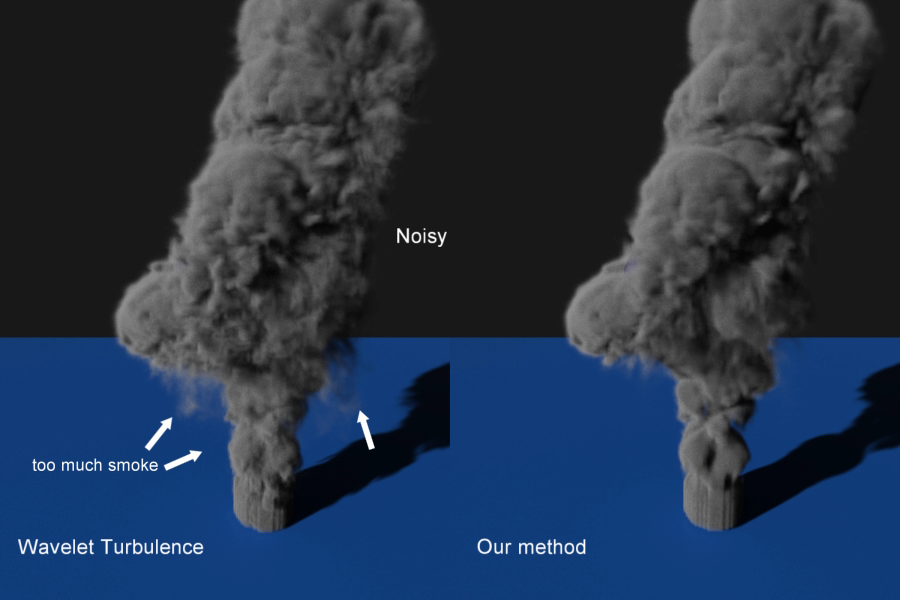
Adding Visual Details Based on Low-Resolution Energy Cascade Ratios for Smoke Simulation
We propose a method for adding visual details to fluid animation while reducing noisy appearances. In grid-based fluid simulations, an issue is that while highly detailed fluids with small eddies can be obtained by increasing the number of grid cells, it costs much more computational time. To addres … Continue reading “Adding Visual Details Based on Low-Resolution Energy Cascade Ratios for Smoke Simulation”
Data-Driven Detailed Hair Animation for Game Characters
We propose a data-driven method to realize high quality detailed hair animations in interactive applications like games. By devising an error metric method to evaluate hair animation similarities, we take hair features into consideration as much as possible. We also propose a novel database construc … Continue reading “Data-Driven Detailed Hair Animation for Game Characters”
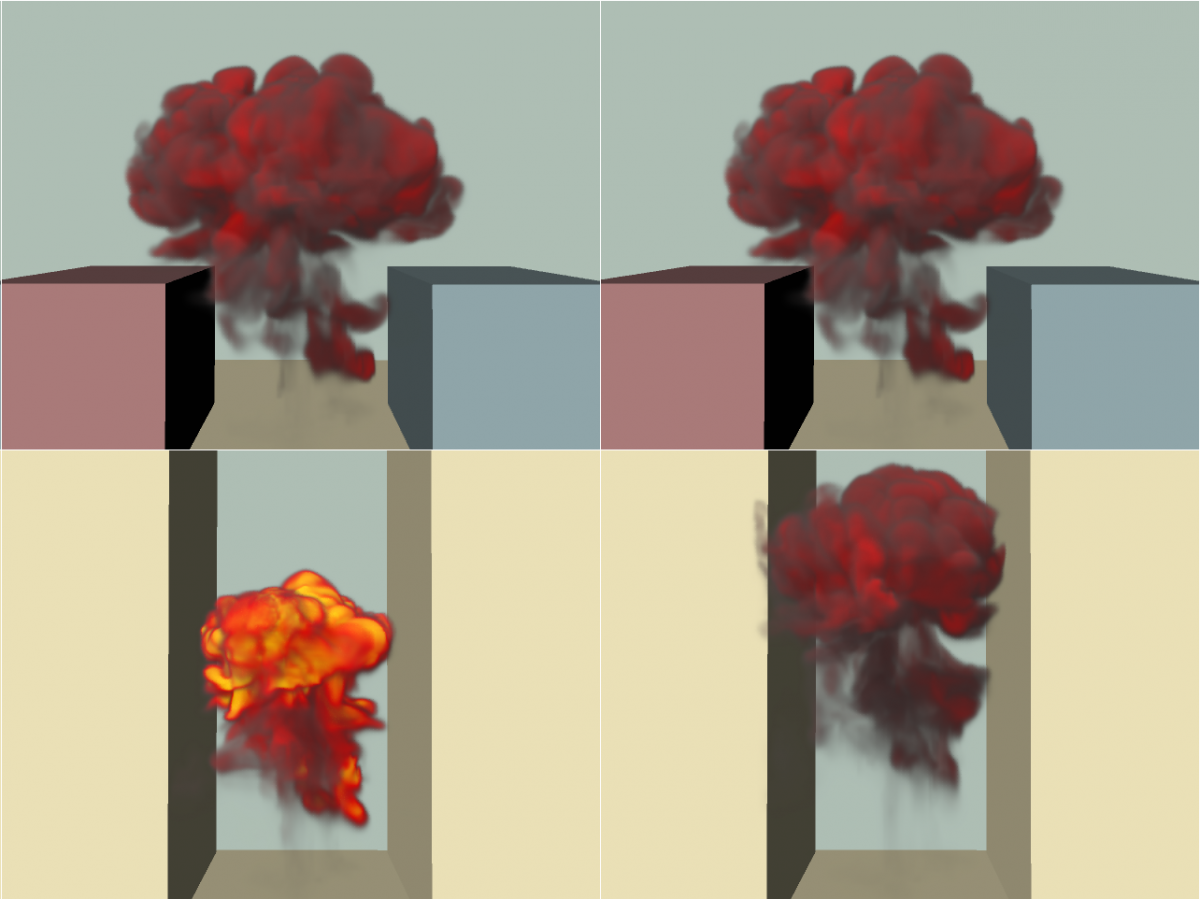
Controlling the Shape and Motion of Plumes in Explosion Simulations
We propose a fluid simulation method with controlling the shape and motion of rising fire and smoke, called plumes, in the incompressible phase of explosion phenomenon. With our method, plumes are generated based on physical phenomenon called entrainment, which strongly characterizes plume behaviors … Continue reading “Controlling the Shape and Motion of Plumes in Explosion Simulations”
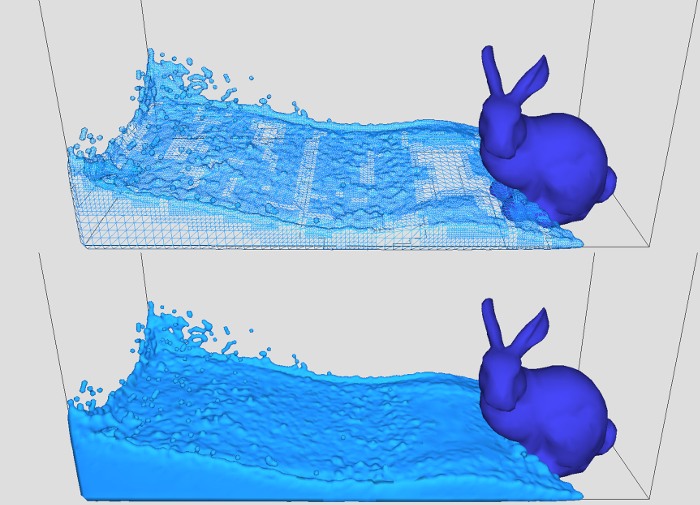
GPU-based Adaptive Surface Reconstruction for Real-time SPH Fluids
We propose a GPU-based adaptive surface reconstruction algorithm for Smoothed-Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) fluids. The adaptive surface is reconstructed from 3-level grids as proposed by [Akinci13]. The novel part of our algorithm is a pattern based approach for crack filling, which is recognized as … Continue reading “GPU-based Adaptive Surface Reconstruction for Real-time SPH Fluids”