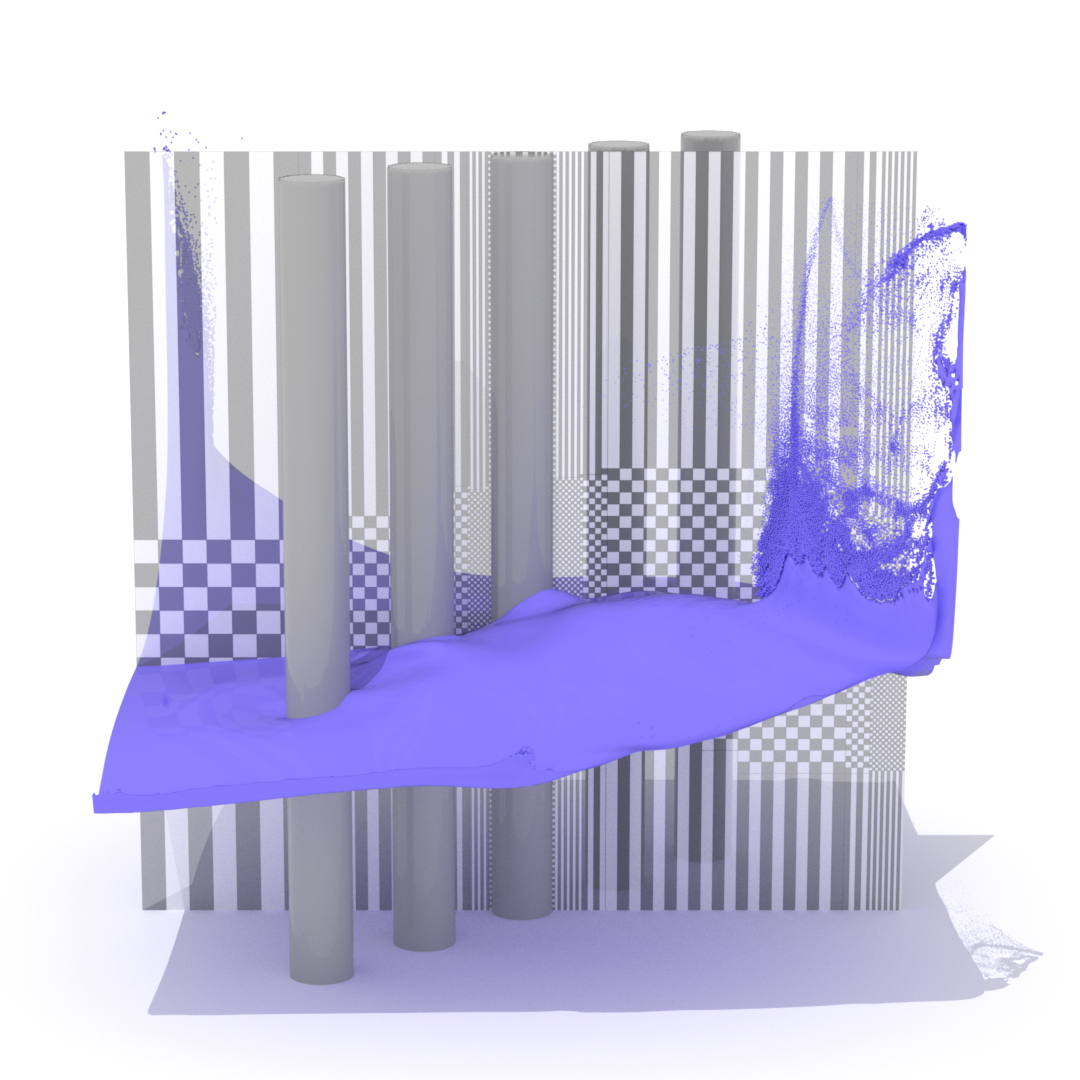
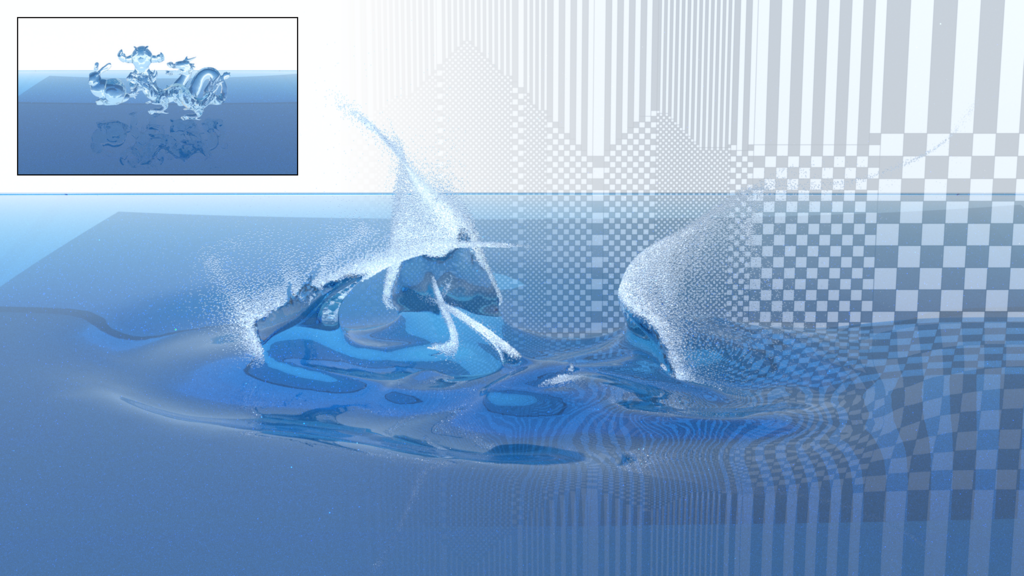
This paper introduces a novel grid structure that extends tall cell methods for efficient deep water simulation. Unlike previous tall cell methods, which are designed to capture all the fine details around liquid surfaces, our approach subdivides tall cells horizontally, allowing for more aggressive adaptivity and a significant reduction in the number of cells. The foundation of our method lies in a new variational formulation of Poisson’s equations for pressure solve tailored for tall-cell grids, which naturally handles the transition of variable-sized cells. This variational view not only permits the use of the efficacy-proven conjugate gradient method but also facilitates monolithic two-way coupled rigid bodies. The key distinction between our method and previous general adaptive approaches, such as tetrahedral or octree grids, is the simplification of adaptive grid construction. Our method performs grid subdivision in a quadtree fashion, rather than an octree. These 2D cells are then simply extended vertically to complete the tall cell population. We demonstrate that this novel form of adaptivity, which we refer to as quadtree tall cells, delivers superior performance compared to traditional uniform tall cells.
Video
Paper
-
Fumiya Narita, Nimiko Ochiai, Takashi Kanai, Ryoichi Ando
Quadtree Tall Cells for Eulerian Liquid Simulation
SIGGRAPH Conference Papers ’25, August 10–14, 2025, Vancouver, BC, Canada.
Paper (author’s version)
DOI
BibTeX
@InProceedings{Narita2025,
author = {Fumiya Narita and Nimiko Ochiai and Takashi Kanai and Ryoichi Ando},
title = {Quadtree Tall Cells for Eulerian Liquid Simulation},
booktitle = {SIGGRAPH Conference Papers ’25},
series = {SIGGRAPH ’25},
year = {2025},
month = {08},
articleno = {10},
numpages = {11},
keywords = {Fluid, Liquid, Tall Grids},
location = {Vancouver, BC, Canada},
isbn = {979-8-4007-1540-2/2025/08},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3721238.3730652},
doi = {10.1145/3721238.3730652},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA}
}
Hindsight
(2025. July) We have realized that some discretization remains unclear, particularly pertaining to the pressure sample locations and the volumetric face areas encoded in the matrices [V], [grad] and [A].
- The vertical positioning of pressure samples (on the y-axis) is illustrated in Figure 2. However, their horizontal locations are not explicitly covered in the paper. For all cells (both cubical and tall) the pressure samples are placed such that, when viewed from above (the xz-plane in Figure 2), they appear centered within the cell.
- The matrices [V], [grad] and [A] encode not only the volumetric areas of cell faces but also the vertical inner ghost area volumes specific to tall cells. See Figure 3(f) from [1], which shows this volume between two vertically stacked pressure samples. During the pressure solve, we temporarily insert a ghost velocity by averaging velocities from the background vertical cell faces. This ghost velocity is used solely for the pressure solve and discarded afterward.
These two insights were found with the help of feedback from Christopher Batty.
[1] Geoffrey Irving, Eran Guendelman, Frank Losasso, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2006. Efficient simulation of large bodies of water by coupling two and three dimensional techniques. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3 (July 2006), 805–811. https://doi.org/10.1145/1141911.1141959